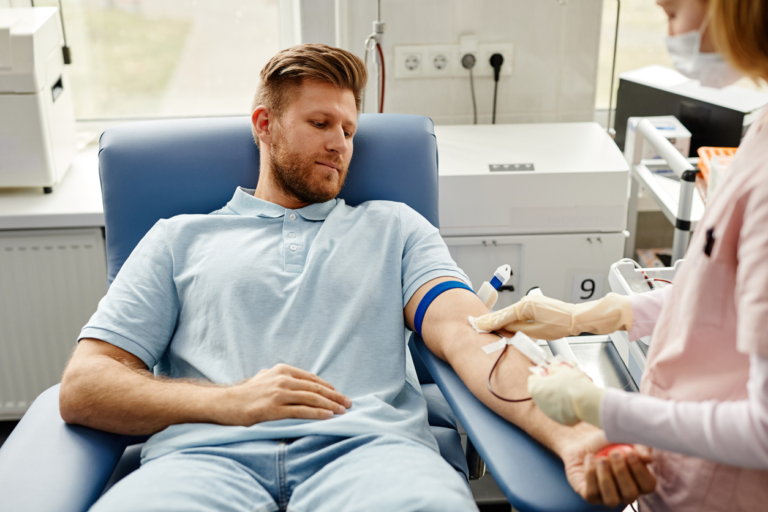
The procedure known as phlebotomy involves taking a patient’s blood for therapeutic purposes. This process is fundamental to healthcare, acting as a basis for diagnosing and managing numerous ailments. Through phlebotomy, medical personnel can collect the blood samples required for laboratory examinations, which yield vital details regarding a patient’s condition.
When they use accurate blood samples, physicians can identify illnesses, track the effectiveness of therapies, and oversee patient care. Additionally, phlebotomy is essential to life-saving procedures such as blood donation and transfusion. Knowing the significance of phlebotomy emphasizes the vital role phlebotomists play in the medical industry.
The Process of Phlebotomy
Several crucial procedures are included in phlebotomy to guarantee patient safety and precise results. It is important to first get the patient ready. Make sure the patient is comfortable, perhaps by seating them in a phlebotomy chair, answering any questions, and describing the procedure. The vein of choice for blood collection should then be chosen; this is typically the inner elbow of the arm. To make the veins more visible, use a tourniquet.
Before starting the procedure, use an antiseptic to clean the puncture site. Then, carefully slide the needle into the vein to extract the required volume of blood. After drawing blood, take out the needle and press on the area to halt any further bleeding. To guarantee proper testing, handle and label the blood samples appropriately. Each stage is essential for the procedure to be both safe and effective.
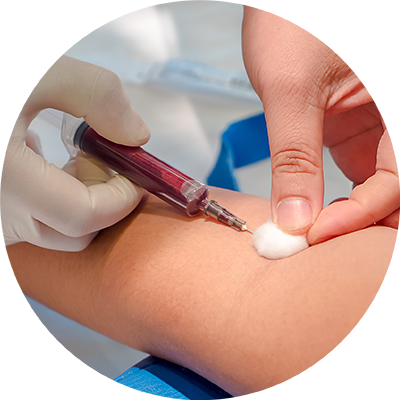
Types of Phlebotomy Procedures
Various processes may be involved in phlebotomy, depending on the goal and the patient’s needs. The most popular technique is venipuncture, where blood is extracted from a vein, usually in the arm. The majority of blood tests and donations follow this process. A capillary puncture is a procedure used to extract a small volume of blood by pricking the heel or finger. It is frequently applied to pediatric patients and used for glucose testing.
Another method is arterial blood gas collection, which involves taking blood from an artery—typically the wrist—to assess the amounts of carbon dioxide and oxygen. Certain methods and equipment are needed for every procedure to guarantee precision and patient comfort. Knowing these many kinds makes choosing the right treatment for every medical circumstance easier.
Phlebotomist Training and Certification
Phlebotomists must complete specialized training and obtain certification. Obtaining a high school diploma or its equivalent is the first requirement. Enroll in a program that will teach you phlebotomy; these courses usually span several months. Important subjects like anatomy, blood collection methods, and safety procedures are covered in the course.
You will obtain practical experience through clinical practice under supervision. After the training, you must pass a test to get certified. Certification can improve your employment prospects and attest to your ability.
A successful career in phlebotomy requires strong attention to detail and effective communication. Maintaining your certification and staying current with the newest practices need ongoing education and training.
The Role of Phlebotomy in Diagnosis
Phlebotomy plays a critical role in disease diagnosis and treatment. Reliable diagnostic tests require accurate blood samples, and phlebotomy done properly guarantees that the samples have accurate information. Numerous diseases, including infections, anemia, diabetes, and more, can be found with these tests. Additionally, blood testing can track long-term illnesses and assess how well a treatment is working. Thanks to phlebotomy, doctors can make well-informed decisions regarding patient treatment.
Phlebotomy aids in early disease detection, efficient treatment, and improved disease management by providing fast and accurate information. It emphasizes how important phlebotomists are to preserving patient health and guaranteeing positive medical outcomes.

Phlebotomy in Blood Donation and Transfusion
In blood donation and transfusion, phlebotomy is essential and helps save lives. Phlebotomists take blood samples from donors during blood donation, ensuring the procedure is secure and effective. After being drawn, the blood is processed, stored, and tested for later use. Phlebotomy ensures patients receive the right kind and quantity of blood during transfusions.
Accurate blood collection and handling are essential to avoid problems and guarantee the security of both donors and receivers. Phlebotomy facilitates numerous medical procedures, surgeries, and emergency treatments by enabling blood donations and transfusions. Phlebotomists are critical in providing life-saving care and ensuring a steady blood flow.
Conclusion
Phlebotomy is essential for research, therapy, and diagnosis since it provides precise blood samples for a range of purposes. To provide patients with optimal care, phlebotomists ensure that blood collection is done safely and effectively.
Their credentials and training demonstrate the experience needed for this important position. Phlebotomy also impacts blood donation and transfusion, saving countless lives. Understanding the significance of phlebotomy and its practitioners highlights their vital role in patient care and overall wellness.