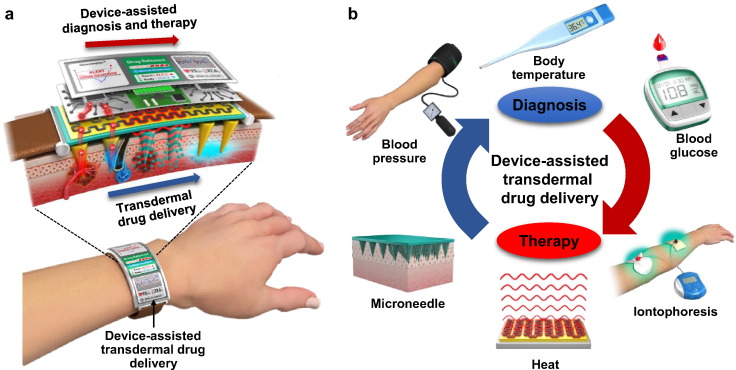
Dermatology and pharmaceuticals, the effective delivery of drugs through the skin—transdermal delivery—has long been a pursuit to maximize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing systemic side effects. Among the array of transdermal delivery methods, topical dermal delivery devices stand out for their ability to enhance formulation efficiency and skin permeation.
Understanding Topical Dermal Delivery Devices:
Topical dermal delivery devices encompass a variety of tools and technologies designed to optimize the delivery of drugs and formulations through the skin. These devices aim to overcome the skin’s natural barrier properties, facilitate drug penetration into the dermal layers, and improve therapeutic efficacy while minimizing systemic exposure and side effects.
Enhancing Formulation Efficiency:
One of the primary objectives of topical dermal delivery device is to enhance the efficiency of drug formulations. By incorporating innovative technologies such as nanoemulsions, liposomes, and microspheres, these devices enable the formulation of drugs in ways that improve their stability, bioavailability, and skin penetration. Additionally, the use of penetration enhancers, surfactants, and other formulation additives can further optimize drug delivery and enhance therapeutic outcomes.
Improving Skin Permeation:
Skin permeation—the process by which drugs penetrate through the various layers of the skin—is a critical factor in topical dermal delivery. Topical dermal delivery devices employ a variety of mechanisms to enhance skin permeation, including physical methods such as microneedle arrays,
ultrasound, and electroporation, as well as chemical approaches such as penetration enhancers and formulation optimization. These mechanisms work synergistically to disrupt the skin barrier and facilitate the transport of drugs into the underlying tissues, thereby improving drug absorption and efficacy.
Advancements and Implications:
Recent advancements in topical dermal delivery devices have revolutionized the field of transdermal drug delivery. Novel technologies such as microneedle patches, hydrogel-based delivery systems, and laser-assisted delivery devices offer unprecedented control over drug delivery parameters, enabling precise and targeted drug administration through the skin.
These advancements have significant implications for the treatment of various dermatological conditions, including acne, psoriasis, eczema, and skin cancer, as well as for the delivery of systemic medications for conditions such as pain management, hormone therapy, and cardiovascular disease.
Future Directions:
Looking ahead, the future of topical dermal delivery devices holds promise for further advancements in drug delivery technology and clinical practice. Continued research and innovation in areas such as nanotechnology, biomaterials, and personalized medicine are expected to drive the development of next-generation delivery devices that offer even greater precision, efficiency, and patient satisfaction.
By harnessing the power of topical dermal delivery devices, clinicians and researchers can unlock new possibilities for the treatment of skin diseases and systemic conditions, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Conclusion:
Topical dermal delivery devices represent a cornerstone of modern transdermal drug delivery, offering enhanced formulation efficiency and skin permeation for improved therapeutic outcomes. With ongoing advancements in technology and research, these devices hold immense promise for transforming the treatment landscape across dermatology and beyond, paving the way for personalized, precise, and effective drug delivery solutions.